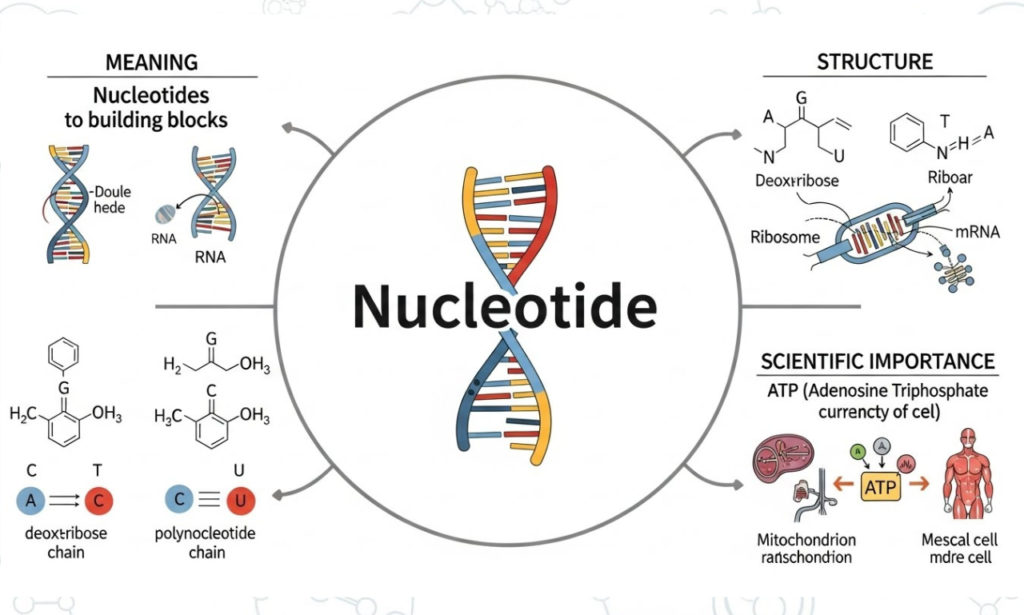
The term Nukleotidy plays an essential role in discussions about genetics, biology, and modern scientific research. Nukleotidy represent the foundational units that make up DNA and RNA—two of the most important molecules in living organisms. Without Nukleotidy, life as we know it would not exist, because these building blocks carry instructions that shape all biological functions. This article explores what Nukleotidy are, how they function, and why they are so important in today’s scientific and technological landscape.
What Are Nukleotidy? A Deep Look Into Their Definition
In biology, Nukleotidy are the small organic molecules that combine to create nucleic acids. These nucleic acids form DNA and RNA, which store genetic information and support essential cellular activities. Each Nukleotid contains three main components:
-
A nitrogenous base
-
A sugar molecule
-
A phosphate group
Together, these components allow Nukleotidy to link and form long, complex chains that carry genetic information across generations.
The Structure of Nukleotidy and How They Work
Understanding the structure of Nukleotidy helps explain their role in genetics. Each Nukleotid consists of several interconnected parts that determine its function.
The Nitrogenous Base
The base is the part of Nukle-otidy that varies. In DNA, these are:
-
Adenine (A)
-
Thymine (T)
-
Cytosine (C)
-
Guanine (G)
In RNA, thymine is replaced by uracil (U).
Sugar Component
Nukle-otidy contain either:
-
Deoxyribose (in DNA)
-
Ribose (in RNA)
The type of sugar determines whether the nucleic acid will form DNA or RNA.
Phosphate Group
The phosphate group links Nukle-otidy together, forming a stable backbone that protects genetic information.
Types of Nukleotidy and Their Biological Roles
Different types of Nukle-otidy serve different purposes in the cell. While their basic structure is similar, each type has a specialized role.
DNA Nukleotidy
These Nukle-otidy store long-term genetic information. They form the double helix structure that carries inherited traits.
RNA Nukleotidy
RNA-based Nukle-otidy help convert genetic information into proteins. They support:
-
Protein synthesis
-
Gene expression
-
Enzyme regulation
Energy-Carrying Nukleotidy
ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is a well-known energy-carrying molecule. It is also a type of Nukleotid that powers cellular processes.
Signaling Nukleotidy
Some Nukle-otidy act as messengers inside the cell, helping transmit signals and regulate various biological functions.
Why Nukleotidy Are Essential for Living Organisms
Nukleotidy provide the instructions for building and maintaining life. Without these molecules, organisms would not have the ability to grow, reproduce, heal, or adapt.
Genetic Information Storage
DNA is made entirely from Nukle-otidy. It contains the blueprint that controls every biological process.
Protein Formation
Nukleo-tidy in RNA guide the creation of proteins, which perform essential tasks such as:
-
Repairing tissues
-
Transporting nutrients
-
Supporting immune function
Cell Division and Growth
When cells divide, Nukle-otidy help copy DNA accurately, ensuring new cells have the correct information.
Energy Transfer
ATP, a type of Nukleotid, is the main energy currency of the cell.
Scientific Applications of Nukleotidy in Modern Research
Researchers use Nukle-otidy in various fields due to their critical role in genetic and molecular processes. Their importance has grown tremendously in biotechnology and health science.
Genetic Engineering
Scientists use altered or synthetic Nukle-otidy to modify genes. This helps in:
-
Developing new crops
-
Treating genetic disorders
-
Studying diseases
DNA Sequencing
Modern sequencing technologies rely on Nukle-otidy to identify genetic patterns. This supports:
-
Disease diagnosis
-
Ancestry tracing
-
Forensic investigations
Medical Research
Nukle-otidy play a key role in developing vaccines, medicines, and targeted therapies.
Synthetic Biology
Researchers create artificial Nukle-otidy to design new biological systems, pushing the boundaries of biotechnology.
Nukleotidy in Everyday Life: Practical Examples
Even though Nukle-otidy are microscopic, their influence reaches into our everyday experiences.
In Medicine and Healthcare
Nukle-otidy help doctors:
-
Detect viruses
-
Understand cancer
-
Create personalized treatments
In Nutrition
Some foods provide essential nutrients that support Nukleotid production in the body.
In Technology
Emerging data storage technologies use nucleic acid principles to store digital information using Nukle-otidy-like structures.
The Role of Nukleotidy in Evolution and Adaptation
Life evolves through changes in Nukle-otidy sequences. These molecules help species adapt over generations.
Mutations and Variation
Small changes in Nukle-otidy create genetic diversity. This allows organisms to evolve and survive environmental shifts.
Natural Selection
Beneficial changes in Nukle-otidy can help organisms become stronger, faster, or more resistant to disease.
Inheritance
Parents pass their Nukle-otidy sequences to their children, maintaining traits across generations.
Modern Innovations Using Nukleotidy
Scientists continue to explore new ways to use Nukleotidy. Their structure and behavior inspire modern tools and technologies.
mRNA Technologies
The recent rise of mRNA science, based on RNA Nukle-otidy, has revolutionized vaccines and medical treatments.
Gene Editing Tools
CRISPR-Cas9 works by recognizing specific Nukle-otidy sequences, allowing precise modification of DNA.
Biocomputing
Researchers are experimenting with computing systems built on Nukle-otidy-like structures for faster, smaller, and more sustainable data storage.
The Future of Nukleotidy in Science and Technology
The importance of Nukleotidy will continue to grow as new innovations emerge.
Expanding Genetic Research
Scientists will uncover more about how Nukle-otidy influence diseases, aging, and human development.
Advanced Biotechnology
Future technologies may rely on synthetic Nukle-otidy to create new forms of medicine, materials, and biological systems.
Health Personalization
Nukle-otidy sequencing may soon allow treatments tailored entirely to an individual’s genetic structure.
Conclusion
Nukle-otidy are the essential molecules that support life, power cellular processes, and carry the genetic instructions that shape every living organism. Their importance spans from biology and medicine to modern technology and biotechnology. As research continues, Nukle-otidy will remain central to understanding life and building the scientific innovations of the future.